Topics API ช่วยให้สามารถโฆษณาตามความสนใจได้โดยไม่ต้องใช้คุกกี้ของบุคคลที่สาม
How the Topics API works
The Topics API can be used to observe and provide access to topics that appear to be of interest to the user, based on their activity. The Topics API can then give API callers (such as ad tech platforms) access to a user's topics of interest, but without revealing additional information about the user's activity.
Key concepts
- A topic is a human-readable topic of interest for the current user and is part of the Topics taxonomy.
- A caller is an entity, such as an app, a third-party SDK, a website, or service, that makes a request to the Topics API to observe or access a user's interests.
- A topic is observed by a caller, if the caller made a Topics API request from a web page or app associated with this topic during the past three epochs.
- An epoch is a period of topic computation, which defaults to one week.
- A taxonomy is a hierarchical list of categories, which includes, for example, such categories as
/Arts & Entertainment/Music & Audio/Soul & R&Band/Business & Industrial/Business Services/Corporate Events. - Topics are derived using a classifier model that maps user activity to zero or more topics.
Topics API flow core steps
The Topics API lifecycle has three main steps:
- Observe user activity, such as when they visit the web page
https://cats.example/tabby/index.htmlor download the appcats. - Derive topics from user activity, for example
/Pets & Animals/Pets/Cats. - Access topics previously observed for the user, for example as a signal to select relevant advertising (such as a cat food promotion).
Observe topics
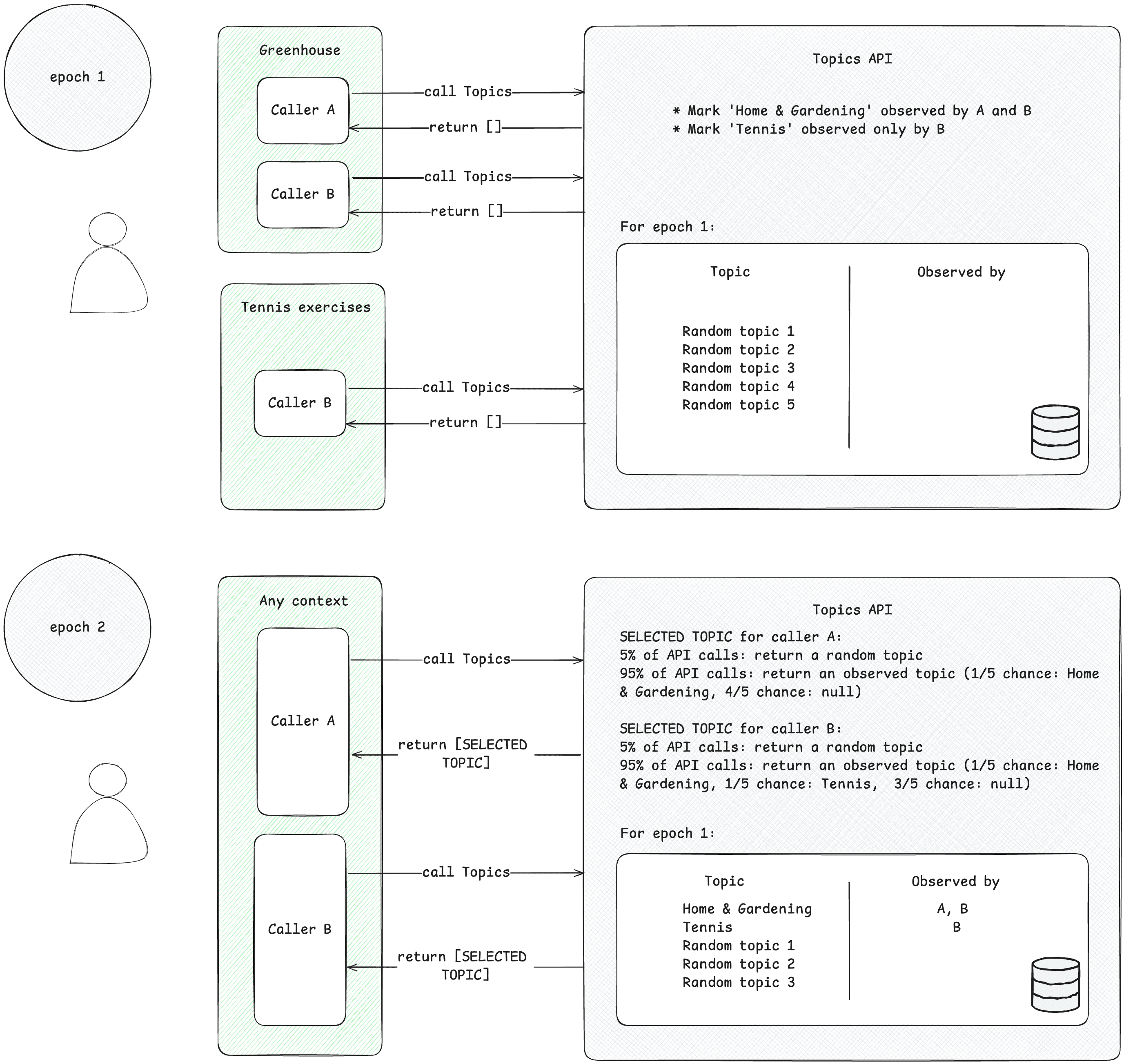
Callers can only access topics of interest that they've observed. A caller observes a topic when they make a Topics API request from a context associated with this topic. To illustrate this concept, consider the following simplified example.
- Suppose there are two Topics API callers: A and B.
- There are two contexts:
- Greenhouse, for example an app named Greenhouse or a website greenhouse.example, associated with the topic
Home & Garden. - Tennis exercises, for example an app named Tennis Exercises or a website tennis.example, associated with the topic
Sports/Tennis.
- Greenhouse, for example an app named Greenhouse or a website greenhouse.example, associated with the topic
- Both caller A and B are present in the context of Greenhouse.
- Only the caller B is present in the context of Tennis exercises.
- Assume that no topics were observed for the user before epoch 1, for the sake of simplification.
- The user visits the Greenhouse app, and callers A and B make a Topics API call to record the user visit to the page or app (see the implementation guide suggested in Next steps to find out how to call the Topics API). This record (a hostname or app data) is later used to derive topics of interest. The Topics API will later mark the topic
Home & Gardenas observed by both callers A and B. - The user visits the Tennis exercises app. Only the caller B sends a Topics API request. The Topics API will later mark the topic
Sports/Tennisas observed by the caller B. - By the end of the epoch, the Topics API refreshes the user's top topics and determines the callers that observed these topics based on user activity.
- Later, when the caller B makes another Topics API call, it can get either
Home & GardenorSports/Tennistopic (or, with a 5% chance, a random topic) for this user in the response array. - Caller A can only access the topic
Home & Garden, as it has never observed the topicSports/Tennis. This means that a third-party will only learn about a user's topic of interest within the specific context (app or website) where it is present.
Derive topics
Topics derives topics of interest from user activity. The topics are selected from a predefined open-source taxonomy. Once per epoch, Topics refreshes the user's top five topics and the callers that observed them during the epoch. The Topics classifier model derives topics from user activity: hostname for a web page visit, app information on Android.
Caller accesses user's topics of interest
The API returns only topics that have been observed by the caller within the most recent three epochs. A maximum of three topics may be returned to a caller,one topic for each of the three recent epochs (if the caller observed topics for that epoch). The returned topics can be used by the caller to supplement any contextual information and can be combined to help find a more relevant ad for the user.
Epochs
The Topics API must ensure that the topics of interest it provides are kept up to date. The topics are inferred for a user based on their activity during a period of time known as an epoch, one week by default. Each user has their own epochs (epochs are "per user") and the initial start time is randomized.
Once each epoch, the Topics API computes the user's top five topics and determines which callers observed those topics using on-device information. The topic selected for each epoch is randomly selected from the user's top five topics for that time period. To further enhance privacy and ensure that all topics may be represented, there is a 5% chance the topic is randomly selected from all possible topics in the taxonomy of interests.
หัวข้อบนเว็บในทางปฏิบัติ
ในเว็บ ระบบจะอนุมานหัวข้อจากชื่อโฮสต์ของหน้าที่ผู้ใช้เข้าชม เช่น หัวข้อที่อนุมานสำหรับเว็บไซต์ dogs.example อาจเป็น /สัตว์เลี้ยง/สัตว์เลี้ยง/สุนัข
แผนภาพต่อไปนี้แสดงตัวอย่างแบบย่อเพื่อสาธิตวิธีที่ Topics API อาจช่วยแพลตฟอร์มเทคโนโลยีโฆษณาเลือกโฆษณาที่เหมาะสม ตัวอย่างนี้ถือว่าเบราว์เซอร์ของผู้ใช้มีโมเดลอยู่แล้วเพื่อแมปชื่อโฮสต์ของเว็บไซต์กับหัวข้อ
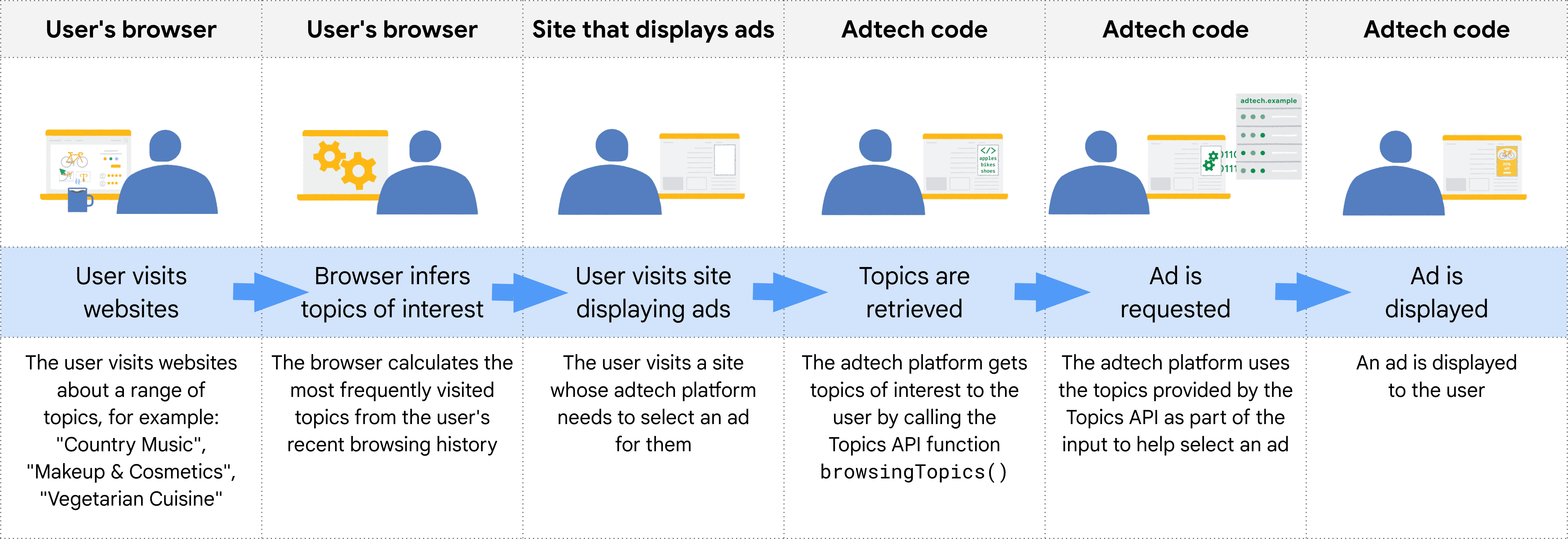
เบราว์เซอร์จะกำหนดต้นทางของผู้เรียกจากบริบทของโค้ดที่เรียกใช้ Topics API ในทางปฏิบัติ หมายความว่าผู้ใช้ Topics จะเรียกใช้ API ใน iframe จากต้นทาง หรือรวมหัวข้อไว้ใน fetch ไปยังต้นทาง
เช่น แพลตฟอร์มฝั่งขาย (SSP) สามารถฝังในเว็บไซต์ของผู้เผยแพร่โฆษณาได้หลายแห่ง จากนั้น SSP จะเรียกใช้ Topics API ภายใน iframe จากต้นทาง ซึ่งจะช่วยให้สามารถสังเกตหัวข้อที่เชื่อมโยงกับผู้ใช้ในเว็บไซต์ของผู้เผยแพร่โฆษณาเหล่านั้นได้ จากนั้นระบบจะแชร์หัวข้อเหล่านี้กับแพลตฟอร์มฝั่งดีมานด์ (DSP) เพื่อช่วยเลือกโฆษณาที่เกี่ยวข้องสําหรับผู้ใช้
วิธีที่ API ตัดสินว่าผู้โทรรายใดจะเห็นหัวข้อใด
ผู้เรียก API จะได้รับเฉพาะหัวข้อที่ได้สังเกตเมื่อเร็วๆ นี้ และระบบจะรีเฟรชหัวข้อสำหรับผู้ใช้ 1 ครั้งในแต่ละ Epoch ซึ่งเป็นระยะเวลาที่กำหนดไว้ 1 สัปดาห์ในการใช้งานของ Chrome ซึ่งหมายความว่า API จะมีช่วงเวลาต่อเนื่องที่ผู้เรียกใช้ที่เฉพาะเจาะจงอาจได้รับหัวข้อที่สังเกตได้
ตารางต่อไปนี้แสดงตัวอย่าง (แม้ว่าจะมีขนาดเล็กอย่างไม่สมจริง) ของประวัติการท่องเว็บสมมติของผู้ใช้ในช่วง Epoch เดียว โดยแสดงหัวข้อที่เชื่อมโยงกับเว็บไซต์ที่ผู้ใช้เข้าชม และผู้เรียก API ที่อยู่ในแต่ละเว็บไซต์ (เอนทิตีที่เรียก document.browsingTopics() ในโค้ด JavaScript ที่รวมอยู่ในเว็บไซต์)
| ไซต์ | หัวข้อ | ผู้เรียก API ในเว็บไซต์ |
|---|---|---|
| running.example | Running & WalkingAthletic Shoes |
adtech1.example adtech2.example |
| dogs.example | Dogs |
adtech1.example |
| holiday.example | Hotels & Accommodations |
adtech2.example |
| sunglasses.example | Sunglasses |
[ไม่มี] |
เมื่อสิ้นสุดช่วงเวลา (โดยค่าเริ่มต้นคือ 1 สัปดาห์) Topics API จะสร้างหัวข้อยอดนิยมของเบราว์เซอร์สำหรับสัปดาห์นั้น
- ตอนนี้ adtech1.example มีสิทธิ์รับหัวข้อ
Running & WalkingAthletic ShoesและDogsเนื่องจากสังเกตเห็นหัวข้อดังกล่าวใน running.example และ dogs.example - adtech1.example ไม่มีสิทธิ์รับ
Hotels & Accommodationsสำหรับผู้ใช้รายนี้ เนื่องจากไม่มีอยู่ในเว็บไซต์ใดๆ ที่ผู้ใช้เข้าชมเมื่อเร็วๆ นี้ซึ่งเชื่อมโยงกับหัวข้อนั้น - adtech2.example เห็นหัวข้อ
Running & Walking,Athletic ShoesและHotels & Accommodationsแต่ไม่เห็นหัวข้อDogs
ผู้ใช้เข้าชม sunglasses.example ซึ่งมีSunglasses แต่ไม่มีการเรียกใช้ Topics API ในเว็บไซต์นั้น ในตอนนี้ การดำเนินการนี้หมายความว่า API จะไม่แสดงผลหัวข้อ Sunglasses สำหรับผู้เรียกใช้รายใดก็ตาม
ในสัปดาห์ที่ 2 ผู้ใช้เข้าชมเว็บไซต์อื่น
| ไซต์ | หัวข้อ | ผู้เรียก API ในเว็บไซต์ |
|---|---|---|
| cameras.example | Camera & Photo Equipment |
adtech2.example |
นอกจากนี้ ระบบยังเพิ่มโค้ดจาก adtech2.example ไปยัง sunglasses.example ด้วย
| ไซต์ | หัวข้อ | ผู้เรียก API ในเว็บไซต์ |
|---|---|---|
| sunglasses.example | Sunglasses |
adtech2.example |
นอกจาก Running & Walking, Athletic Shoes และ Hotels & Accommodations จากสัปดาห์ที่ 1 แล้ว การดำเนินการนี้หมายความว่าตอนนี้ adtech2.example จะรับหัวข้อ Camera & Photo Equipment และ Sunglasses ได้ แต่จะรับได้ก็ต่อเมื่อถึงยุคถัดไป ซึ่งก็คือสัปดาห์ที่ 3 เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าบุคคลที่สามจะไม่สามารถทราบข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับอดีตของผู้ใช้ (ในกรณีนี้คือความสนใจในแฟชั่น) มากกว่าที่ทราบได้จากคุกกี้
หลังจากผ่านไปอีก 2 สัปดาห์ Running & Walking Athletic Shoes และ Hotels & Accommodations อาจหลุดออกจากรายการหัวข้อที่มีสิทธิ์ของ adtech2.example หากผู้ใช้ไม่ได้เข้าชมเว็บไซต์ที่มีหัวข้อเหล่านั้นซึ่งมีโค้ดจาก adtech2.example
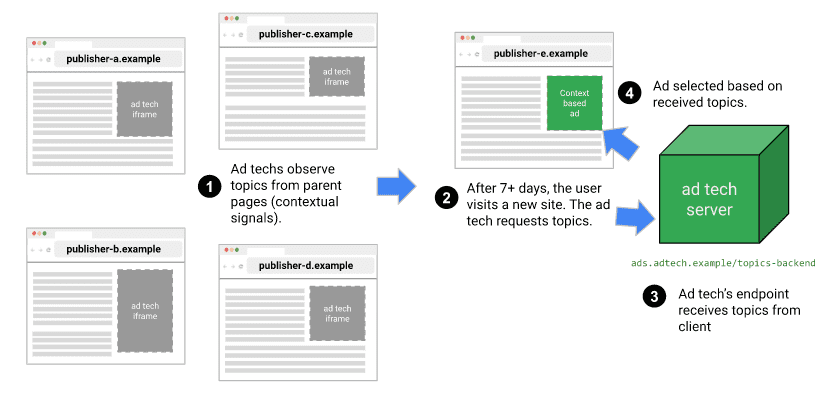
โมเดลตัวแยกประเภท
Topics ใช้โมเดลตัวแยกประเภทที่แมปชื่อโฮสต์ของเว็บไซต์กับหัวข้อตั้งแต่ 0 รายการขึ้นไป (การวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม เช่น URL แบบเต็มหรือเนื้อหาหน้าเว็บ อาจช่วยให้แสดงโฆษณาที่เกี่ยวข้องมากขึ้น แต่ก็อาจลดความเป็นส่วนตัวลงด้วย)
การจัดหมวดหมู่
ระบบจะเลือกหัวข้อจากอนุกรมวิธาน Chrome เป็นผู้ดูแลจัดการหัวข้อเหล่านี้ โดยมีเป้าหมายเพื่อให้การจัดหมวดหมู่กลายเป็นแหล่งข้อมูลที่ได้รับการดูแลโดยผู้มีส่วนร่วมในระบบนิเวศที่เชื่อถือได้ อนุกรมวิธานต้องมีขนาดเล็กพอที่เบราว์เซอร์ของผู้ใช้จำนวนมากจะเชื่อมโยงกับแต่ละหัวข้อ เป้าหมายสุดท้ายคือการให้การจัดหมวดหมู่มาจากบุคคลภายนอกที่รวมความคิดเห็นและแนวคิดจากทั่วทั้งอุตสาหกรรม
หากต้องการหลีกเลี่ยงหมวดหมู่ที่ละเอียดอ่อน หัวข้อต้องเป็นแบบสาธารณะ ดูแลจัดการโดยเจ้าหน้าที่ และเป็นข้อมูลล่าสุดอยู่เสมอ การจัดหมวดหมู่ที่ Chrome ใช้ได้รับการดูแลจัดการโดยมนุษย์เพื่อยกเว้นหมวดหมู่ที่โดยทั่วไปถือว่าละเอียดอ่อน เช่น ชาติพันธุ์หรือรสนิยมทางเพศ
การจัดประเภทหัวข้อ
เราดูแลจัดการหัวข้อสำหรับเว็บไซต์ยอดนิยม 50,000 เว็บไซต์ด้วยตนเอง และใช้รายการแทนที่ที่ดูแลจัดการของชื่อโฮสต์และหัวข้อนี้เพื่อฝึกโมเดลตัวแยกประเภท สำหรับเว็บไซต์ยอดนิยม ระบบจะเข้าถึงหัวข้อจากรายการลบล้างแทนที่จะใช้โมเดลตัวแยกประเภท คุณดูรายการการลบล้างได้ในคอมพิวเตอร์
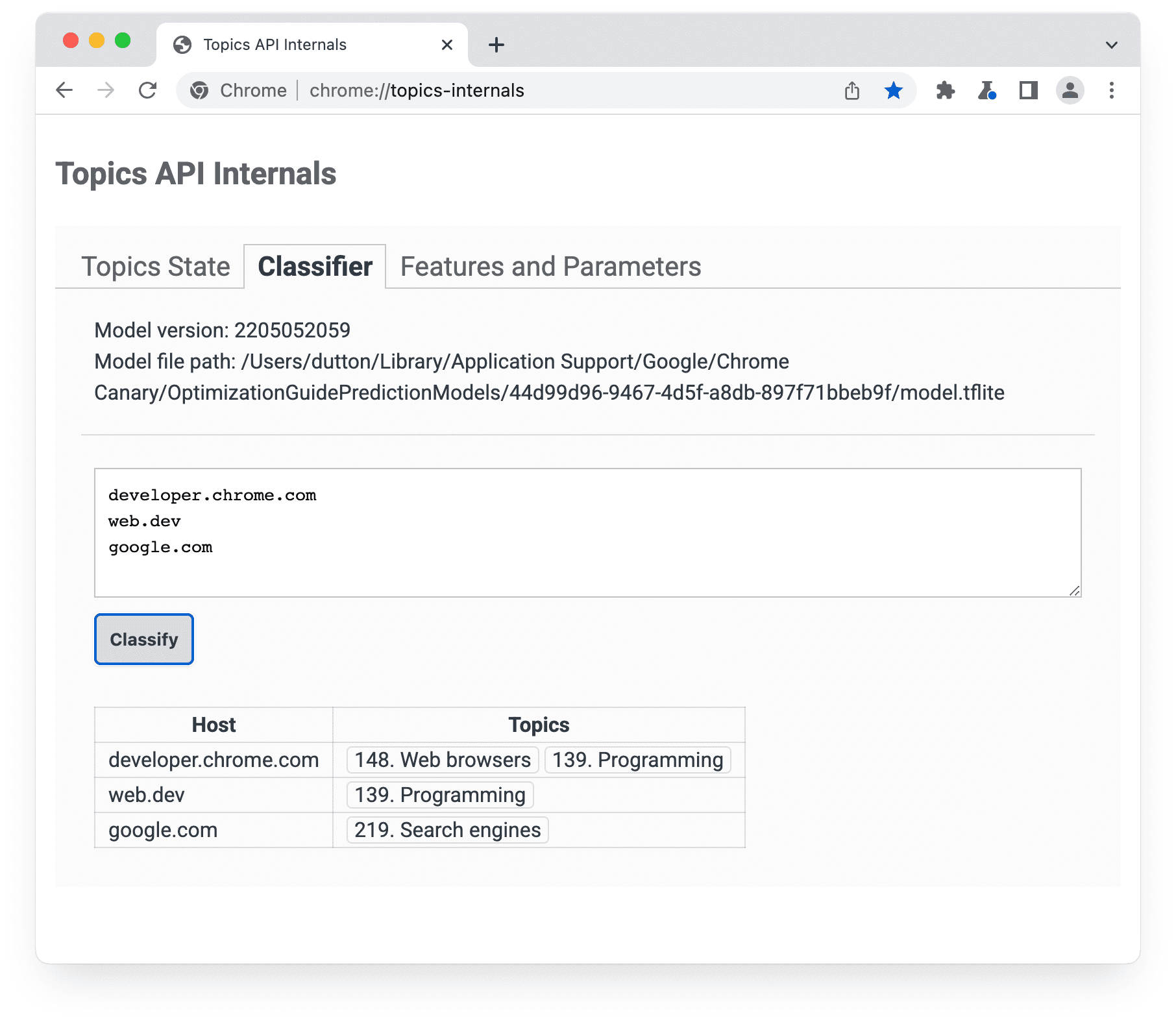
chrome://topics-internals จะแสดงเวอร์ชันของโมเดล เส้นทาง และหัวข้อที่เชื่อมโยงกับแต่ละโฮสต์ที่แสดงการติดตั้งใช้งาน Topics API ของ Chrome จะดาวน์โหลดไฟล์ TensorFlow Lite ที่แสดงถึงโมเดลเพื่อให้ใช้ในเครื่องบนอุปกรณ์ของผู้ใช้ได้
วิธีกำหนด 5 หัวข้อยอดนิยมของผู้ใช้
API จะแสดงผล 1 หัวข้อสำหรับแต่ละ Epoch โดยแสดงผลได้สูงสุด 3 หัวข้อ หากระบบแสดงผล 3 รายการ จะรวมถึงหัวข้อสำหรับ Epoch ปัจจุบันและ 2 Epoch ก่อนหน้า
- เมื่อสิ้นสุดแต่ละยุค เบราว์เซอร์จะรวบรวมรายการหน้าเว็บที่ตรงตามเกณฑ์ต่อไปนี้
- ผู้ใช้เข้าชมหน้าเว็บในระหว่างช่วงเวลา
- หน้าเว็บมีโค้ดที่เรียกใช้
document.browsingTopics() - API เปิดใช้แล้ว (เช่น ผู้ใช้หรือส่วนหัวของการตอบกลับไม่ได้บล็อก)
- เบราว์เซอร์ในอุปกรณ์ของผู้ใช้จะใช้โมเดลตัวแยกประเภทที่ Topics API จัดเตรียมไว้ให้เพื่อแมปชื่อโฮสต์ของแต่ละหน้ากับรายการหัวข้อ
เบราว์เซอร์จะสร้างรายการหัวข้อ 5 อันดับแรก
- ระบบจะกำหนดหัวข้อรูททั้ง 22 หัวข้อในอนุกรมวิธานให้กับกลุ่ม "มีประโยชน์สูง" หรือ "มีประโยชน์มาตรฐาน" โดยอิงตามความคิดเห็นจากระบบนิเวศการโฆษณา เบราว์เซอร์จะจัดเรียงหัวข้อตามการกำหนดกลุ่มก่อน หัวข้อลูกหลานทั้งหมดจะรับการกำหนดกลุ่มของหัวข้อรูทหลัก ระบบจะจัดลำดับความสำคัญของหัวข้อที่มี "ประโยชน์สูง"
- จากนั้นเบราว์เซอร์จะจัดเรียงหัวข้อตามความถี่ภายในแต่ละที่เก็บข้อมูล
- ระบบจะเลือก 5 หัวข้อแรกจากรายการที่จัดเรียงนี้เป็นหัวข้อยอดนิยมของผู้ใช้สำหรับ Epoch นั้น
จากนั้นdocument.browsingTopics()จะแสดงหัวข้อแบบสุ่มจาก 5 หัวข้อยอดนิยมสำหรับแต่ละ Epoch โดยมีโอกาส 5% ที่ระบบจะสุ่มเลือกหัวข้อใดก็ได้จากอนุกรมวิธานของหัวข้อทั้งหมด ใน Chrome ผู้ใช้ยังนำหัวข้อแต่ละรายการออกหรือล้างประวัติการท่องเว็บเพื่อลดจำนวนหัวข้อที่ API แสดงได้ด้วย ผู้ใช้ยังเลือกไม่ใช้ API ได้ด้วย
คุณดูข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับหัวข้อที่สังเกตได้ในระหว่าง Epoch ปัจจุบันได้จากหน้า chrome://topics-internals
Next steps
Setup
Implement Topics
ดูเพิ่มเติม
ดูแหล่งข้อมูลของเราเพื่อทำความเข้าใจเกี่ยวกับ Topics API บนเว็บให้ดียิ่งขึ้น
- ลองดูวิดีโอเดโม วิดีโอที่ทำร่วมกัน และวิดีโอคำแนะนำแบบทีละขั้นจาก Topics
- ดูรายการ Flag ของ Chrome ที่อนุญาตให้นักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ปรับแต่ง Topics API สำหรับการทดสอบ
- ดูวิธีที่ผู้ใช้และนักพัฒนาแอปควบคุม API ได้
- ดูแหล่งข้อมูลสําหรับคำอธิบายและการสนับสนุนทางเทคนิค ถามคำถาม มีส่วนร่วม และแชร์ความคิดเห็น


