Topics API를 사용하면 서드 파티 쿠키를 사용하지 않고도 관심 기반 광고를 게재할 수 있습니다.
Topics API 작동 방식
Topics API는 사용자의 활동을 기반으로 사용자에게 관심이 있는 것으로 보이는 주제를 관찰하고 액세스 권한을 제공하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다. 그러면 Topics API는 API 호출자 (예: 광고 기술 플랫폼)에게 사용자의 관심 주제에 대한 액세스 권한을 부여할 수 있지만 사용자의 활동에 관한 추가 정보는 공개하지 않습니다.
주요 개념
- 주제는 현재 사용자의 관심 주제이며 인간이 읽을 수 있으며 주제 분류의 일부입니다.
- 호출자는 Topics API에 사용자의 관심분야를 관찰하거나 액세스하도록 요청하는 앱, 서드 파티 SDK, 웹사이트, 서비스와 같은 항목입니다.
- 호출자가 지난 3 에포크 동안 이 주제와 연결된 웹페이지 또는 앱에서 Topics API 요청을 보낸 경우 주제는 호출자가 관찰합니다.
- 에포크는 주제 계산 기간으로 기본값은 1주일입니다.
- 분류는
/Arts & Entertainment/Music & Audio/Soul & R&B및/Business & Industrial/Business Services/Corporate Events와 같은 카테고리를 포함하는 계층 구조의 카테고리 목록입니다. - 주제는 사용자 활동을 0개 이상의 주제에 매핑하는 분류기 모델을 사용하여 파생됩니다.
Topics API 흐름 핵심 단계
Topics API 수명 주기는 다음 세 가지 주요 단계로 구성됩니다.
- 사용자가 웹페이지
https://cats.example/tabby/index.html를 방문하거나 앱cats을 다운로드하는 경우와 같은 사용자 활동을 관찰합니다. - 사용자 활동(예:
/Pets & Animals/Pets/Cats)에서 주제를 파생합니다. - 이전에 사용자에 관해 관찰된 주제 액세스입니다(예: 관련성 있는 광고(예: 고양이 사료 프로모션)를 선택하기 위한 신호).
주제 관찰
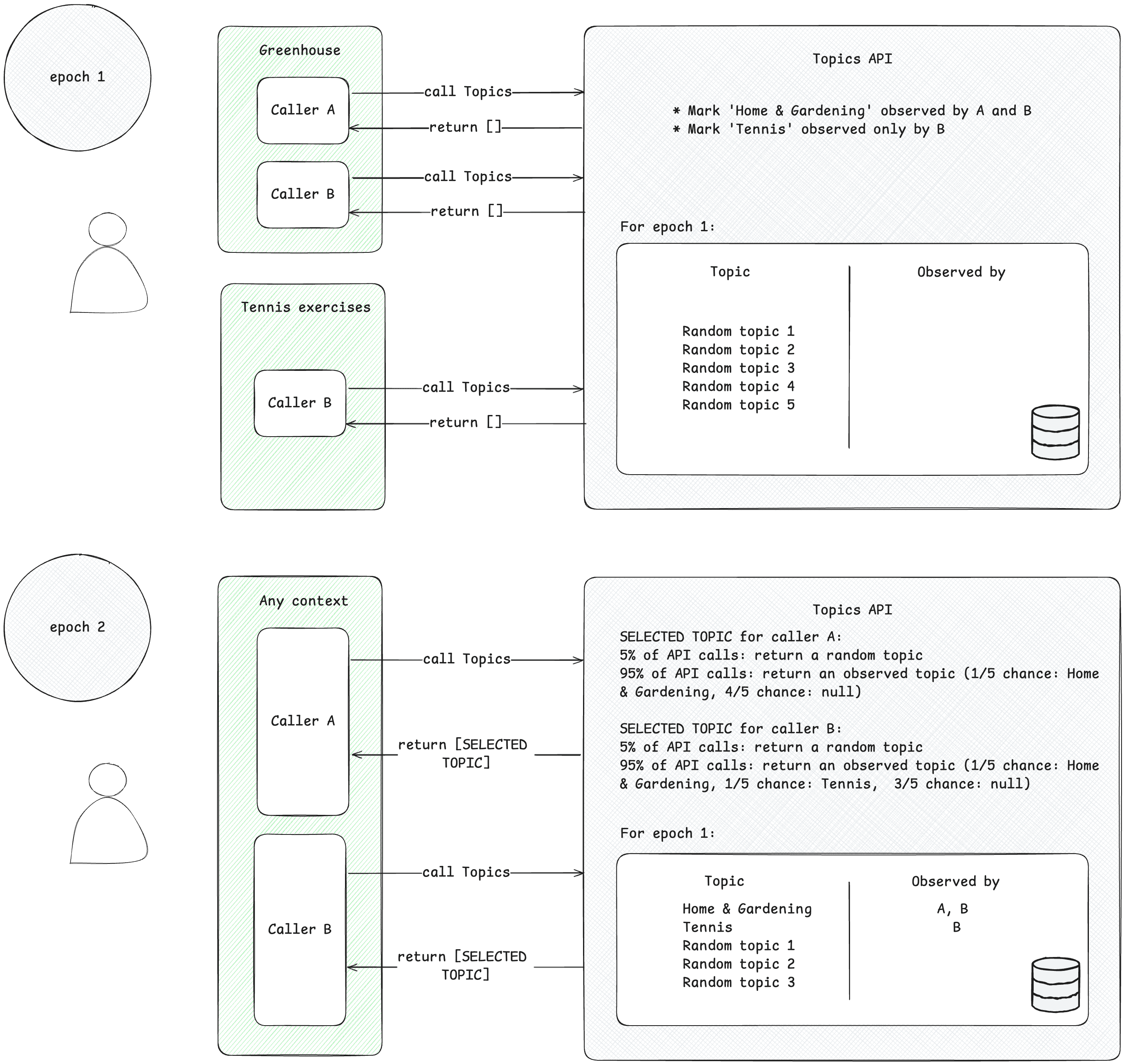
호출자는 관찰한 관심 주제에만 액세스할 수 있습니다. 호출자는 이 주제와 연결된 컨텍스트에서 Topics API 요청을 보낼 때 주제를 관찰합니다. 이 개념을 설명하기 위해 다음과 같은 단순화된 예시를 살펴보겠습니다.
- Topics API 호출자가 A와 B 두 개 있다고 가정해 보겠습니다.
- 두 가지 컨텍스트가 있습니다.
- Greenhouse(예: Greenhouse라는 앱 또는
Home & Garden주제와 연결된 웹사이트 greenhouse.example). - 테니스 운동:
Sports/Tennis주제와 연결된 Tennis Exercises라는 앱 또는 tennis.example 웹사이트를 예로 들 수 있습니다.
- Greenhouse(예: Greenhouse라는 앱 또는
- 호출자 A와 B가 모두 Greenhouse 컨텍스트에 있습니다.
- 호출자 B만 테니스 연습 컨텍스트에 있습니다.
- 편의상 에포크 1 이전에는 사용자에 대해 관찰된 주제가 없다고 가정합니다.
- 사용자가 Greenhouse 앱을 방문하고 호출자 A와 B가 Topics API를 호출하여 페이지 또는 앱 방문을 기록합니다 (Topics API를 호출하는 방법을 알아보려면 다음 단계에 제안된 구현 가이드를 참고하세요). 이 레코드 (호스트 이름 또는 앱 데이터)는 나중에 관심 주제를 파생하는 데 사용됩니다. 나중에 Topics API는 주제
Home & Garden를 호출자 A와 B가 모두 관찰한 것으로 표시합니다. - 사용자가 테니스 운동 앱을 방문합니다. 호출자 B만 Topics API 요청을 보냅니다. 나중에 Topics API는 주제
Sports/Tennis를 호출자 B가 관찰한 것으로 표시합니다. - 에포크가 끝날 때 Topics API는 사용자의 인기 주제를 새로고침하고 사용자 활동을 기반으로 이러한 주제를 관찰한 호출자를 결정합니다.
- 나중에 호출자 B가 Topics API를 다시 호출하면 응답 배열에서 이 사용자의
Home & Garden또는Sports/Tennis주제 (또는 5% 의 확률로 임의의 주제)를 가져올 수 있습니다. - 호출자 A는 주제
Sports/Tennis를 관찰한 적이 없으므로 주제Home & Garden에만 액세스할 수 있습니다. 즉, 서드 파티는 사용자가 관심을 두는 주제가 있는 특정 맥락 (앱 또는 웹사이트) 내에서만 이를 알 수 있습니다.
주제 도출
Topics는 사용자 활동에서 관심 주제를 파생합니다. 주제는 사전 정의된 오픈소스 분류에서 선택합니다. Topics는 에포크당 한 번씩 사용자의 상위 5개 주제와 에포크 중에 이를 관찰한 호출자를 새로고침합니다. Topics 분류 기준 모델은 웹페이지 방문의 호스트 이름, Android의 앱 정보와 같은 사용자 활동에서 주제를 파생합니다.
호출자가 사용자의 관심 주제에 액세스함
API는 최근 3개 에포크 내에서 호출자가 관찰한 주제만 반환합니다. 호출자에게 최대 3개의 주제가 반환될 수 있으며,최근 3개 에포크당 하나의 주제가 반환됩니다 (호출자가 해당 에포크의 주제를 관찰한 경우). 반환된 주제는 호출자가 문맥 정보를 보완하는 데 사용할 수 있으며 사용자에게 더 관련성 높은 광고를 찾는 데 도움이 되도록 결합될 수 있습니다.
에포크
Topics API는 제공하는 관심 주제를 최신 상태로 유지해야 합니다. 주제는 에포크(기본적으로 1주일)라는 기간 동안의 활동을 기반으로 사용자를 위해 추론됩니다. 각 사용자는 자체 에포크를 가지며 (에포크는 '사용자별') 초기 시작 시간은 무작위로 지정됩니다.
Topics API는 각 에포크에 한 번씩 사용자의 상위 5개 주제를 계산하고 기기 내 정보를 사용하여 이러한 주제를 관찰한 호출자를 결정합니다. 각 에포크의 주제는 해당 기간 동안 사용자가 가장 많이 살펴본 5개의 주제 중에서 무작위로 선택됩니다. 개인 정보 보호를 강화하는 한편 모든 주제가 표시되도록 하기 위해, 관심분야 분류에서 선택 가능한 모든 주제 중 특정 주제가 무작위로 선택될 확률은 5% 로 되어 있습니다.
웹 주제 실습
웹에서는 사용자가 방문하는 페이지의 호스트 이름에서 주제가 추론됩니다. 예를 들어 dogs.example 웹사이트에 대해 추론된 주제는 /Pets & Animals/Pets/Dogs일 수 있습니다.
다음 다이어그램은 광고 기술 플랫폼에서 적절한 광고를 선택하는 데 Topics API를 사용하는 방법을 간단한 예를 통해 보여줍니다. 이 예에서는 사용자의 브라우저에 이미 웹사이트 호스트 이름을 주제에 매핑하는 모델이 있다고 가정합니다.
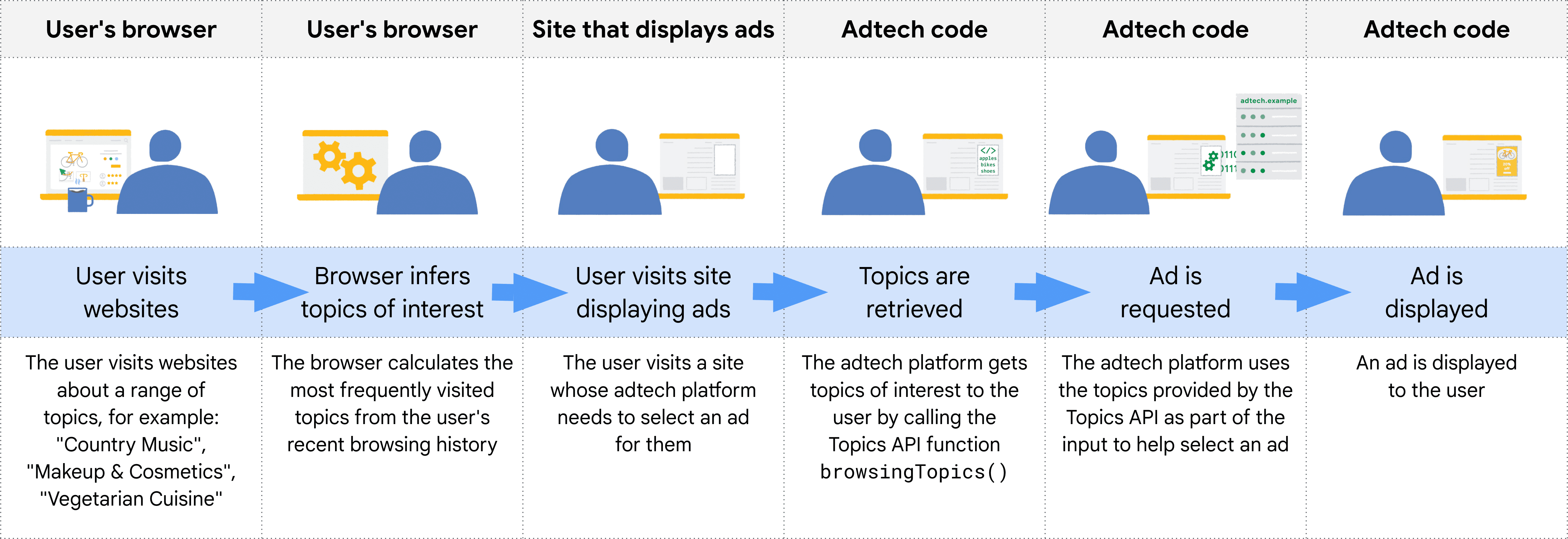
브라우저는 Topics API를 호출하는 코드의 컨텍스트에서 호출자의 출처를 확인합니다. 실제로는 Topics 사용자가 출처의 iframe에서 API를 호출하거나 출처의 가져오기에 주제를 포함합니다.
예를 들어 공급측 플랫폼 (SSP)은 여러 게시자 사이트에 삽입할 수 있습니다. 그러면 SSP는 출처의 iframe 내에서 Topics API를 호출하여 게시자 사이트에서 사용자와 연결된 주제를 관찰할 수 있습니다. 이러한 주제를 수요측 플랫폼 (DSP)과 공유하여 사용자에게 관련성 높은 광고를 선택할 수 있습니다.
API가 어떤 호출자에게 어떤 주제를 표시할지 결정하는 방법
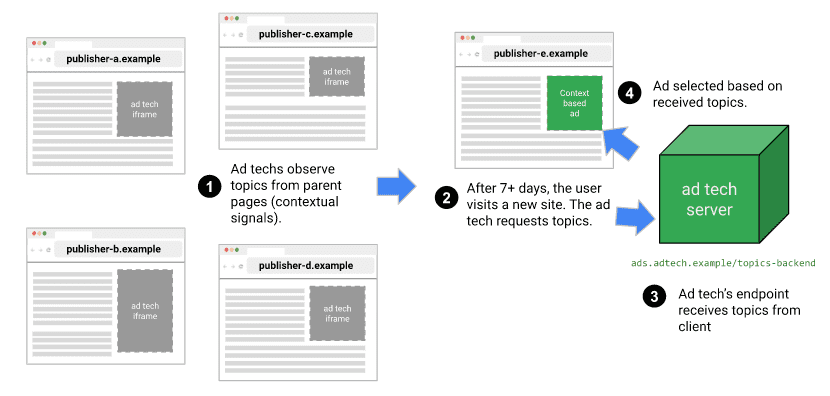
API 호출자는 최근에 관찰한 주제만 수신하며 사용자의 주제는 에포크마다 한 번씩 새로고침됩니다. 에포크는 Chrome 구현에서 1주일로 설정된 기간입니다. 즉, API는 정해진 호출자가 관찰된 주제를 수신할 수 있는 롤링 시간을 제공합니다.
다음 표는 단일 에포크 동안 사용자의 가상 방문 기록의 예시를 보여줍니다 (비현실적으로 작음). 방문한 사이트와 연결된 주제와 각 사이트에 있는 API 호출자 (사이트에 포함된 JavaScript 코드에서 document.browsingTopics()를 호출하는 항목)를 보여줍니다.
| 사이트 | 주제 | 사이트의 API 호출자 |
|---|---|---|
| running.example | Running & WalkingAthletic Shoes |
adtech1.example adtech2.example |
| dogs.example | Dogs |
adtech1.example |
| holiday.example | Hotels & Accommodations |
adtech2.example |
| sunglasses.example | Sunglasses |
[없음] |
에포크 종료 시 (기본적으로 1주일) Topics API가 일주일 동안 브라우저의 상위 주제를 생성합니다.
- adtech1.example은 running.example과 dogs.example에서
Running & Walking,Athletic Shoes,Dogs를 관찰했으므로 이제Running & Walking,Athletic Shoes,Dogs주제를 수신할 수 있습니다. - adtech1.example은
Hotels & Accommodations주제와 관련되어 있으며 최근에 사용자가 방문한 사이트에 존재하지 않았으므로 이 사용자의 주제로Hotels & Accommodations을 수신할 수 없습니다. - adtech2.example은
Running & Walking,Athletic Shoes,Hotels & Accommodations주제를 관찰했으나Dogs주제는 관찰하지 않았습니다.
사용자가 Sunglasses 주제가 있는 sunglasses.example을 방문했지만, 이 사이트에서 Topics API를 호출하지 않았습니다. 이때 API는 호출자에게 Sunglasses 주제를 반환하지 않습니다.
2주 차에 사용자가 다른 사이트를 방문합니다.
| 사이트 | 주제 | 사이트의 API 호출자 |
|---|---|---|
| cameras.example | Camera & Photo Equipment |
adtech2.example |
또한 adtech2.example의 코드가 sunglasses.example에 추가되어 있습니다.
| 사이트 | 주제 | 사이트의 API 호출자 |
|---|---|---|
| sunglasses.example | Sunglasses |
adtech2.example |
adtech2.example은 1주 차에 Running & Walking, Athletic Shoes, Hotels & Accommodations을 수신했으며 이제 Camera & Photo Equipment, Sunglasses 주제도 수신할 수 있게 되나 다음 에포크인 3주 차가 되어야 합니다. 즉, 서드 파티가 쿠키를 사용할 때보다 사용자의 과거 정보 (이 경우 패션에 대한 관심)를 더 자세히 알 수 없습니다.
사용자가 adtech2.example의 코드가 포함되어 있으며 주제가 Running & Walking, Athletic Shoes, Hotels & Accommodations인 사이트를 방문하지 않을 경우 2주 후 Running & Walking, Athletic Shoes, Hotels & Accommodations이 adtech2.example의 대상 주제 목록에서 삭제될 수 있습니다.
분류 모델
Topics는 웹사이트 호스트 이름을 0개 이상의 주제에 매핑하는 분류기 모델을 사용합니다. 전체 URL 또는 페이지 콘텐츠와 같은 추가 정보를 분석하면 더 관련성 높은 광고를 게재할 수 있지만 개인 정보 보호에 부정적인 영향을 줄 수도 있습니다.
분류
주제는 분류에서 선택합니다. 이러한 주제는 분류를 신뢰할 수 있는 생태계 기여자가 관리하는 리소스로 만드는 것을 목표로 Chrome에서 선별했습니다. 분류는 많은 사용자의 브라우저가 각 주제와 연결될 수 있을 만큼 작아야 합니다. 최종 목표는 업계 전반의 의견과 아이디어를 통합하는 외부 당사자로부터 분류를 가져오는 것입니다.
민감한 카테고리를 피하기 위해 주제는 공개되어야 하며, 사람이 직접 선별하고 업데이트해야 합니다. Chrome에서 사용하는 분류는 인종, 성적 지향 등 일반적으로 민감한 것으로 간주되는 카테고리를 제외하기 위해 사람이 선별했습니다.
주제 분류
주제는 상위 사이트 50,000개를 대상으로 수동으로 선별되며, 선별된 호스트 이름 및 주제 재정의 목록은 분류 모델을 학습하는 데 사용됩니다. 인기 사이트의 경우 분류 기준 모델을 사용하는 대신 재정의 목록에서 주제에 액세스합니다. 컴퓨터에서 로컬로 재정의 목록을 확인할 수 있습니다.
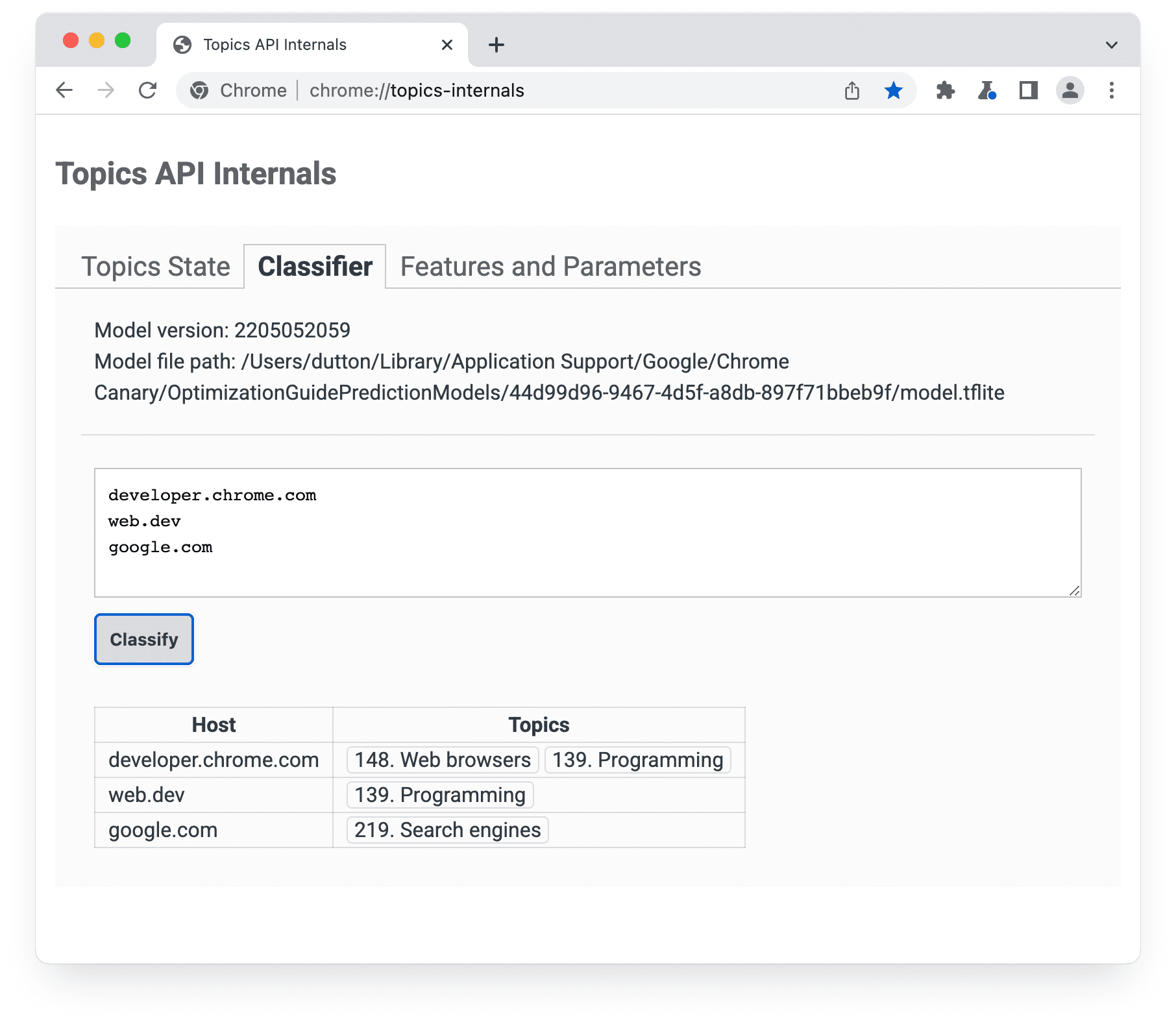
chrome://topics-internals 페이지 분류기 패널에는 모델 버전, 경로, 나열된 각 호스트와 연결된 주제가 표시됩니다.Chrome의 Topics API 구현은 모델을 나타내는 TensorFlow Lite 파일을 다운로드하여 사용자 기기에서 로컬로 사용할 수 있도록 합니다.
사용자의 상위 주제 5개가 선정되는 방식
API는 에포크당 하나씩 최대 3개의 주제를 반환합니다. 3개가 반환되면 여기에는 현재 에포크의 주제 한 개와 이전 에포크의 주제 2개가 포함됩니다.
- 각 에포크가 끝나면 브라우저는 다음 기준을 충족하는 페이지 목록을 컴파일합니다.
- 에포크 동안 사용자가 방문한 페이지입니다.
- 페이지에
document.browsingTopics()를 호출하는 코드가 포함되어 있습니다. - API가 사용 설정됨 (예: 사용자가 또는 응답 헤더로 차단하지 않음)
- 사용자 기기의 브라우저가 Topics API에서 제공하는 분류기 모델을 사용하여 각 페이지의 호스트 이름을 주제 목록에 매핑합니다.
그런 다음 document.browsingTopics() 메서드는 에포크마다 상위 5개 중에서 주제를 무작위로 반환합니다. 이때 전체 주제 분류에서 무작위로 선택될 가능성은 5% 입니다. Chrome에서 사용자는 개별 주제를 삭제하거나 방문 기록을 삭제하여 API에서 반환되는 주제의 수를 줄일 수도 있습니다. 사용자는 API를 선택 해제할 수도 있습니다.
chrome://topics-internals 페이지에서 현재 시대에 관찰된 주제에 관한 정보를 볼 수 있습니다.
다음 단계
참고 항목
웹에서 Topics API를 더 잘 이해하려면 리소스를 확인하세요.
- 주제 데모, 공동작업, 둘러보기 동영상을 확인하세요.
- 개발자가 테스트를 위해 Topics API를 맞춤설정할 수 있는 Chrome 플래그 목록을 참고하세요.
- 사용자와 개발자가 API를 제어하는 방법을 알아보세요.
- 기술 설명 및 지원은 리소스를 확인하세요. 질문하고, 참여하고, 의견을 공유하세요.



