تتيح Topics API عرض الإعلانات المستندة إلى الاهتمامات بدون استخدام ملفات تعريف الارتباط الخارجية.
طريقة عمل Topics API
يمكن استخدام Topics API لمراقبة المواضيع التي يبدو أنّها تهمّ المستخدم وتوفير إمكانية الوصول إليها استنادًا إلى نشاطه. يمكن أن تمنح Topics API بعد ذلك لمستخدمي واجهة برمجة التطبيقات (مثل منصات تكنولوجيا الإعلان) إذن الوصول إلى مواضيع اهتمام المستخدم، ولكن بدون الكشف عن معلومات إضافية عن نشاط المستخدم.
المفاهيم الرئيسية
- الموضوع هو موضوع يهمّ المستخدم الحالي ويمكن لشخص عادي قراءته، وهو جزء من تصنيف المواضيع.
- المُرسِل هو كيان، مثل تطبيق أو حزمة تطوير برامج (SDK) تابعة لجهة خارجية أو موقع إلكتروني أو خدمة، يُرسِل طلبًا إلى Topics API لمراقبة اهتمامات المستخدم أو الوصول إليها.
- يرصد مُرسِل الطلب موضوعًا إذا أرسل طلبًا إلى Topics API من صفحة ويب أو تطبيق مرتبطَين بهذا الموضوع خلال الفترات الثلاث الماضية.
- الفاصل الزمني هو فترة احتساب المواضيع، ويكون تلقائيًا أسبوعًا واحدًا.
- التصنيف هو قائمة هرمية للفئات، تشمل على سبيل المثال فئات مثل
/Arts & Entertainment/Music & Audio/Soul & R&Bو/Business & Industrial/Business Services/Corporate Events. - يتم استنتاج المواضيع باستخدام نموذج مصنّف يربط نشاط المستخدِم بمواضيع معدومة أو أكثر.
الخطوات الأساسية لمسار Topics API
تتضمّن دورة حياة Topics API ثلاث خطوات رئيسية:
- مراقبة نشاط المستخدِم، مثل زيارته لصفحة الويب
https://cats.example/tabby/index.htmlأو تنزيل التطبيقcats - استنباط المواضيع من نشاط المستخدِم، على سبيل المثال
/Pets & Animals/Pets/Cats - الوصول إلى المواضيع التي تم رصدها سابقًا للمستخدم، على سبيل المثال، كإشارة لاختيار إعلانات ذات صلة (مثل إعلان ترويجي لطعام القطط)
مراقبة المواضيع
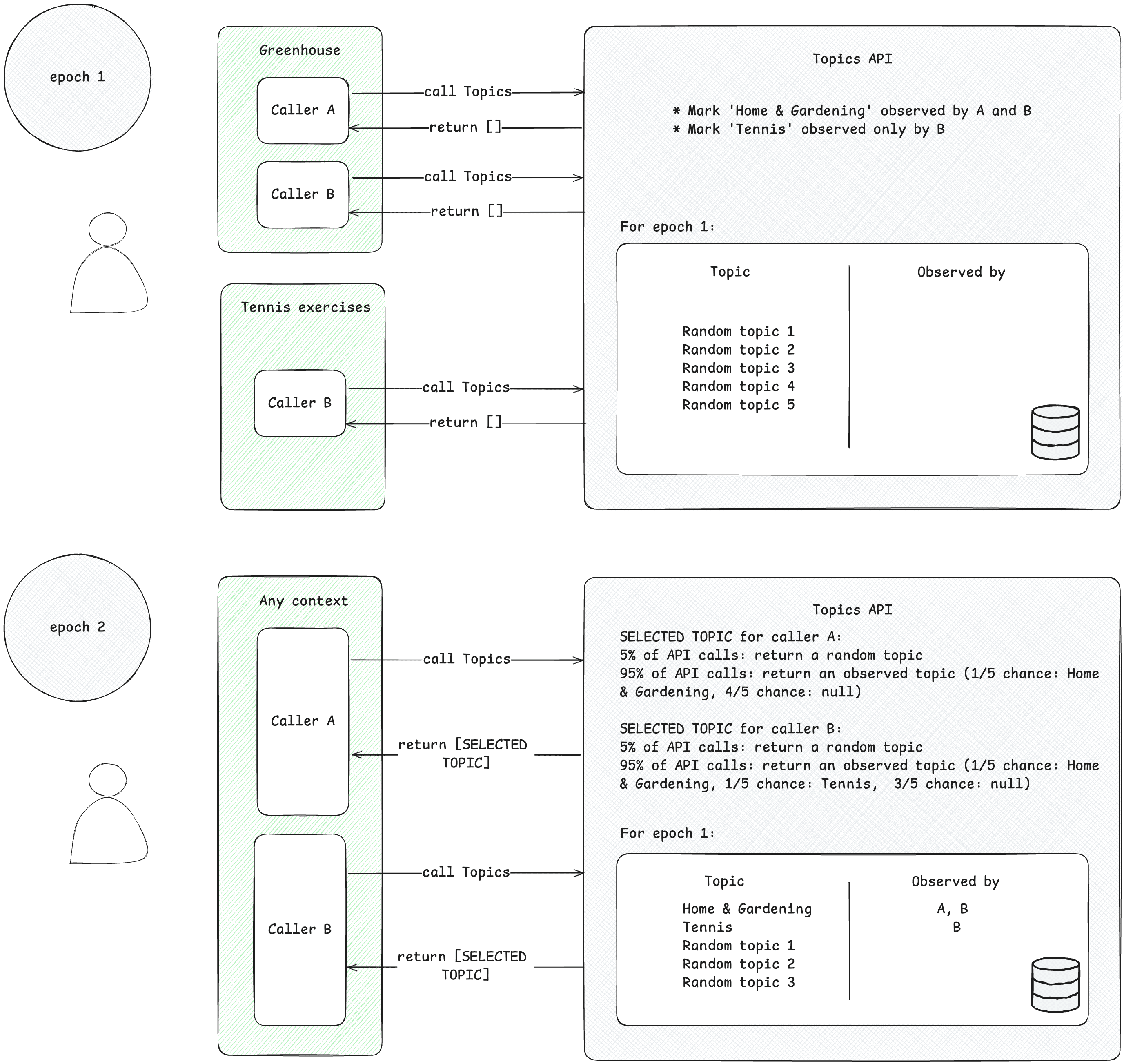
لا يمكن للمتصلين الوصول إلا إلى المواضيع التي تهمّهم والتي لاحظوها. يرصد المُرسِل موضوعًا عند تقديم طلب Topics API من سياق مرتبط بهذا الموضوع. لتوضيح هذا المفهوم، راجِع المثال المبسّط التالي.
- لنفترض أنّ هناك مقدّمَي طلبات بيانات من Topics API: أ وب.
- هناك سياقان:
- Greenhouse، على سبيل المثال، تطبيق باسم Greenhouse أو موقع إلكتروني greenhouse.example، مرتبط بالموضوع
Home & Garden. - تمارين التنس، على سبيل المثال تطبيق باسم "تمارين التنس" أو موقع إلكتروني tennis.example، مرتبط بالموضوع
Sports/Tennis
- Greenhouse، على سبيل المثال، تطبيق باسم Greenhouse أو موقع إلكتروني greenhouse.example، مرتبط بالموضوع
- يظهر كل من المتصلَين أ وب في سياق Greenhouse.
- لا يظهر سوى المتصل ب في سياق تمارين التنس.
- لنفترض أنّه لم يتم رصد أي مواضيع للمستخدم قبل الحقبة 1، وذلك للتبسيط.
- يزور المستخدِم تطبيق Greenhouse، ويُجري المُتصلان أ وب طلبًا إلى Topics API لتسجيل زيارة المستخدِم إلى الصفحة أو التطبيق (اطّلِع على دليل التنفيذ المقترَح في الخطوات التالية لمعرفة كيفية طلب Topics API). ويتم استخدام هذا السجلّ (اسم مضيف أو بيانات التطبيق) لاحقًا لاستخراج المواضيع التي تهمّك. ستضع واجهة برمجة التطبيقات Topics API لاحقًا علامة على الموضوع
Home & Gardenعلى أنّه موضوع رصده كلّ من أ وب. - يزور المستخدم تطبيق تمارين التنس. ولا يرسل سوى المُتصل ب طلبًا إلى Topics API. ستضع Topics API لاحقًا علامة على الموضوع
Sports/Tennisعلى أنّه موضوع رصده المُطلِب B. - بحلول نهاية الحقبة، تُعدّل Topics API أهم مواضيع المستخدِم وتحدِّد المُتصلين الذين رصدوا هذه المواضيع استنادًا إلى نشاط المستخدِم.
- لاحقًا، عندما يُجري المُتصل B طلبًا آخر من Topics API، يمكن أن يحصل على موضوع
Home & GardenأوSports/Tennis(أو موضوع عشوائي بنسبة% 5) لهذا المستخدم في صفيف الاستجابة. - لا يمكن للمتصل أ الوصول إلا إلى الموضوع
Home & Garden، لأنّه لم يرصد الموضوعSports/Tennisمطلقًا. وهذا يعني أنّ الجهة الخارجية لن تعرف سوى موضوع اهتمام المستخدم ضمن السياق المحدّد (التطبيق أو الموقع الإلكتروني) الذي يظهر فيه.
استخراج المواضيع
تستنِد Topics إلى نشاط المستخدِم لتحديد المواضيع التي تهمّه. يتم اختيار المواضيع من تصنيف مفتوح المصدر محدّد مسبقًا. مرّة واحدة في كل حقبة، تُعدّل ميزة "المواضيع" أهم خمسة مواضيع للمستخدم والمتصلين الذين لاحظوها خلال الحقبة. يستنِد نموذج المصنِّف في Topics إلى نشاط المستخدم لتحديد المواضيع: اسم المضيف لزيارة صفحة ويب، ومعلومات التطبيق على Android.
وصول المتصل إلى المواضيع التي تهمّ المستخدم
لا تعرض واجهة برمجة التطبيقات سوى المواضيع التي رصدها المُرسِل خلال آخر ثلاث حقب. يمكن عرض ثلاثة مواضيع كحدّ أقصى للمتصل، موضوع واحد لكلّ من الحقب الثلاث الأخيرة (إذا لاحظ المتصل مواضيع لهذه الحقبة). يمكن للمتصل استخدام المواضيع التي يتم عرضها كملء لأي معلومات سياقية، ويمكن دمجها للمساعدة في العثور على إعلان أكثر صلة بالمستخدم.
الفترات
يجب أن تضمن Topics API تحديث المواضيع التي تهمّك. يتم استنتاج المواضيع للمستخدم استنادًا إلى نشاطه خلال فترة زمنية تُعرَف باسم "الحقبة"، والتي تكون أسبوعًا واحدًا تلقائيًا. يكون لكل مستخدم فترات تدريب خاصة به (تكون الفترات التدريبية "لكل مستخدم") ويتم اختيار وقت البدء الأولي بشكل عشوائي.
بعد كل حقبة، تحتسب Topics API أهم خمسة مواضيع للمستخدم وتحدّد المتصلين الذين لاحظوا هذه المواضيع باستخدام المعلومات على الجهاز فقط. يتم اختيار موضوع كل حقبة بشكل عشوائي من بين أهم خمسة مواضيع للمستخدم في هذه الفترة الزمنية. لتعزيز الخصوصية بشكل أكبر وضمان تمثيل جميع المواضيع، هناك احتمال بنسبة% 5 أن يتم اختيار الموضوع عشوائيًا من بين جميع المواضيع المحتمَلة في تصنيف الاهتمامات.
المواضيع على الويب في الممارسة العملية
على الويب، يتم استنتاج المواضيع من أسماء المضيفين للصفحات التي يزورها المستخدم. على سبيل المثال، قد يكون الموضوع الذي تم استنتاجه للموقع الإلكتروني dogs.example هو /الحيوانات الأليفة والحيوانات/الحيوانات الأليفة/الكلاب.
يعرض الرسم البياني التالي مثالاً مبسطًا لتوضيح كيف يمكن أن تساعد Topics API إحدى منصات تكنولوجيا الإعلان في اختيار إعلان مناسب. يفترض المثال أنّ متصفّح المستخدم يتضمّن نموذجًا لتحديد المواضيع من أسماء مضيفي المواقع الإلكترونية.
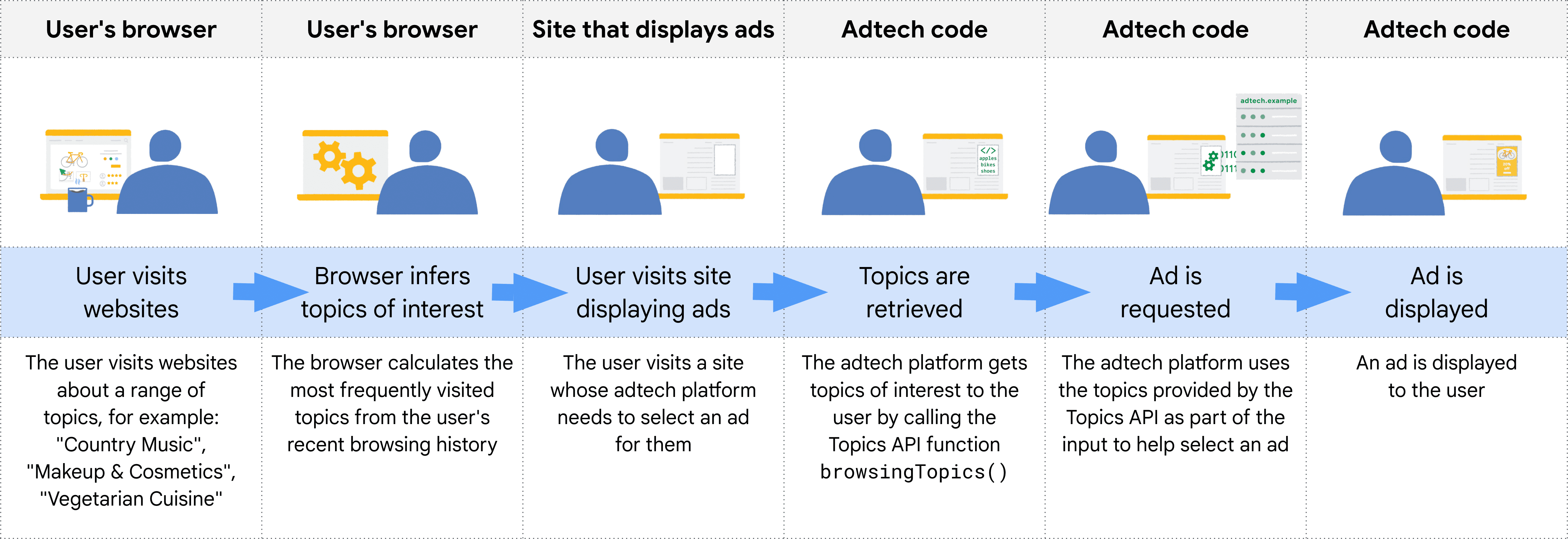
يحدّد المتصفّح مصدر الجهة الطالبة من سياق الرمز الذي يستدعي Topics API. يعني ذلك عمليًا أنّ مستخدمي Topics يطلبون واجهة برمجة التطبيقات في إطار iframe من مصدرهم أو يضمّنون المواضيع في عملية fetch إلى مصدرهم.
على سبيل المثال، يمكن تضمين وسيط عرض إعلانات الموردين (SSP) في مواقع إلكترونية متعددة للناشرين. يمكن بعد ذلك لوسيط عرض إعلانات الموردين طلب Topics API ضمن إطار iframe من مصدرها، ما يتيح لها مراقبة المواضيع المرتبطة بمستخدم على مواقع الناشرين هذه. ويمكن بعد ذلك مشاركة هذه المواضيع مع منصة عرض طلب (DSP) لمساعدتها في اختيار إعلان ملائم بالمستخدِم.
الطريقة التي تحدّد بها واجهة برمجة التطبيقات المواضيع التي تظهر للمتصلين
لا يتلقّى مستدعو واجهة برمجة التطبيقات سوى المواضيع التي رصدها مؤخرًا، ويتم تجديد مواضيع المستخدم مرة واحدة كل حقبة، وهي فترة زمنية تم ضبطها على أسبوع واحد في تنفيذ Chrome. وهذا يعني أنّ واجهة برمجة التطبيقات توفّر نافذة متجددة يمكن من خلالها أن يتلقّى طالب البيانات مواضيع تم رصدها.
يوضّح الجدول التالي مثالاً (صغيرًا بشكل غير واقعي) لسجلّ تصفّح افتراضي لمستخدم خلال فترة واحدة، ويعرض المواضيع المرتبطة بالمواقع الإلكترونية التي زارها، والجهات التي تطلب البيانات من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات والموجودة على كل موقع إلكتروني (الكيانات التي تطلب البيانات من document.browsingTopics() في رمز JavaScript المُضمّن في الموقع الإلكتروني).
| الموقع الإلكتروني | المواضيع | الجهات التي تطلب بيانات من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات على الموقع الإلكتروني |
|---|---|---|
| running.example | Running & WalkingAthletic Shoes |
adtech1.example adtech2.example |
| dogs.example | Dogs |
adtech1.example |
| holiday.example | Hotels & Accommodations |
adtech2.example |
| sunglasses.example | Sunglasses |
[لا شيء] |
في نهاية الفترة الزمنية (أسبوع واحد تلقائيًا)، تنشئ Topics API أهم المواضيع في المتصفّح لهذا الأسبوع.
- أصبح النطاق adtech1.example مؤهلاً الآن لتلقّي المواضيع
Running & WalkingوAthletic ShoesوDogs، لأنّه رصدها على running.example وعلى dogs.example أيضًا. - إنّ adtech1.example غير مؤهَّل لتلقّي الموضوع
Hotels & Accommodationsلهذا المستخدم لأنّه غير متوفّر على أيّ من المواقع الإلكترونية التي زارها المستخدم مؤخرًا والمرتبطة بهذا الموضوع. - اطّلع النطاق adtech2.example على المواضيع
Running & WalkingوAthletic ShoesوHotels & Accommodations، ولكنّه لم يطّلع على الموضوعDogs.
زار المستخدم الموقع الإلكتروني sunglasses.example الذي يتضمّن الموضوع Sunglasses، ولكن لم يتم إجراء أي طلبات إلى Topics API على هذا الموقع الإلكتروني. في هذه المرحلة، يعني ذلك أنّ موضوع Sunglasses لن تعرضه واجهة برمجة التطبيقات لأي طالب.
في الأسبوع الثاني، ينتقل المستخدِم إلى موقع إلكتروني آخر:
| الموقع الإلكتروني | المواضيع | الجهات التي تطلب بيانات من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات على الموقع الإلكتروني |
|---|---|---|
| cameras.example | Camera & Photo Equipment |
adtech2.example |
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، تتم إضافة رمز من adtech2.example إلى sunglasses.example:
| الموقع الإلكتروني | المواضيع | الجهات التي تطلب بيانات من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات على الموقع الإلكتروني |
|---|---|---|
| sunglasses.example | Sunglasses |
adtech2.example |
بالإضافة إلى Running & Walking وAthletic Shoes وHotels & Accommodations من الأسبوع الأول، يعني ذلك أنّ adtech2.example سيتمكّن الآن من تلقّي المواضيع Camera & Photo Equipment وSunglasses، ولكن لن يحدث ذلك إلا في الفترة التالية، أي الأسبوع الثالث. ويضمن ذلك ألا تتمكّن الجهات الخارجية من معرفة المزيد عن اهتمامات المستخدم السابقة (في هذه الحالة، الاهتمام بالموضة) أكثر مما يمكنها معرفته باستخدام ملفات تعريف الارتباط.
بعد أسبوعين آخرين، قد تتم إزالة Running & Walking وAthletic Shoes وHotels & Accommodations من قائمة المواضيع المؤهَّلة في adtech2.example إذا لم يزر المستخدم أي مواقع إلكترونية تتضمّن هذه المواضيع وتتضمّن رمزًا من adtech2.example.
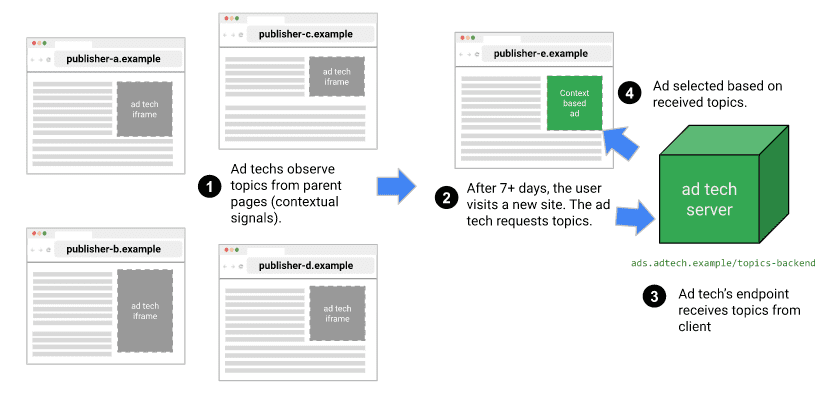
نموذج المصنِّف
تستخدِم Topics نموذج تصنيف يربط أسماء المضيفين للمواقع الإلكترونية بموضوع واحد أو أكثر (قد تتيح إضافة معلومات أخرى، مثل عناوين URL الكاملة أو محتوى الصفحة، عرض إعلانات أكثر صلة بالموضوع، ولكن قد يؤدي ذلك أيضًا إلى الحدّ من الخصوصية).
التصنيف
يتم اختيار المواضيع من تصنيف. وقد اختار Chrome هذه المواضيع بهدف أن يصبح التصنيف مرجعًا يديره مساهمون موثوق بهم في المنظومة المتكاملة. يجب أن يكون التصنيف صغيرًا بما يكفي لربط متصفّحات العديد من المستخدمين بكل موضوع. والهدف النهائي هو أن يتم الحصول على التصنيف من جهة خارجية تدمج الملاحظات والآراء والأفكار الواردة من مختلف الجهات في المجال.
لتجنُّب الفئات الحسّاسة، يجب أن تكون المواضيع علنية ومنظَّمة بتدخّل فريقنا ومحدّثة باستمرار. تم تنظيم التصنيف الذي يستخدمه Chrome من قِبل فريقنا لاستبعاد الفئات التي تُعتبر حساسة بشكل عام، مثل العرق أو الميول الجنسي.
تصنيف المواضيع
يتم تنظيم المواضيع يدويًا لأهم 50,000 موقع إلكتروني، ويتم استخدام قائمة التجاوز المنظَّمة هذه لأسماء المضيفين والمواضيع لتدريب نموذج المصنّف. بالنسبة إلى أهم المواقع الإلكترونية، يتم الوصول إلى المواضيع من قائمة التجاوز بدلاً من استخدام نموذج المصنِّف. يمكنك عرض قائمة التجاوز محليًا على جهاز الكمبيوتر.
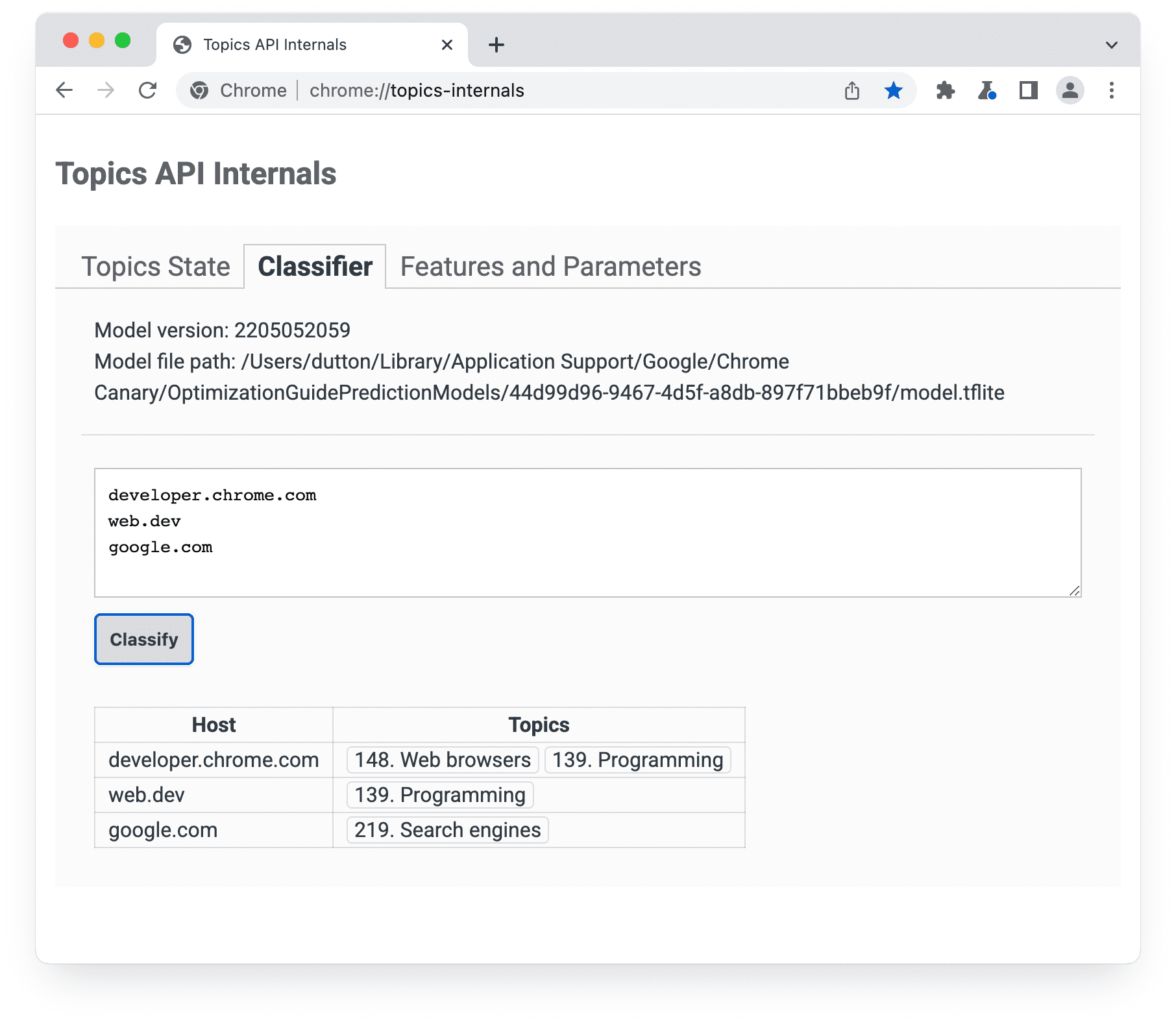
chrome://topics-internals إصدار النموذج ومساره والمواضيع المرتبطة بكل مضيف مُدرَج.عند تنفيذ Topics API في Chrome، يتم تنزيل ملف TensorFlow Lite يمثّل النموذج ليتم استخدامه محليًا على جهاز المستخدم.
كيفية اختيار أهم خمسة مواضيع للمستخدم
تعرض واجهة برمجة التطبيقات موضوعًا واحدًا لكل حقبة، بحد أقصى ثلاثة مواضيع. إذا تم عرض ثلاث مواضيع، سيشمل ذلك مواضيع الحقبة الحالية والحقبتين السابقتين.
- في نهاية كل حقبة، يجمع المتصفّح قائمة بالصفحات التي تستوفي المعايير التالية:
- زار المستخدم الصفحة خلال الفترة الزمنية.
- تتضمّن الصفحة رمزًا يستدعي
document.browsingTopics(). - تم تفعيل واجهة برمجة التطبيقات (على سبيل المثال، لم يحظرها المستخدم أو عنوان الاستجابة).
- يستخدم المتصفّح على جهاز المستخدم نموذج التصنيف الذي توفّره Topics API لربط اسم المضيف لكل صفحة بقائمة مواضيع.
ينشئ المتصفّح قائمة بأبرز خمسة مواضيع.
- يتمّ تصنيف كلّ موضوع من المواضيع الرئيسية الـ 22 في التصنيف ضمن حزمة "مستوى فائدة عالٍ" أو "مستوى فائدة عادي" استنادًا إلى الملاحظات الواردة من منظومة الإعلانات المتكاملة. يرتّب المتصفّح المواضيع أولاً حسب تصنيفها في الحزمة. ترث جميع المواضيع الفرعية تصنيف المجموعة الخاص بموضوعها الرئيسي. يتم منح الأولوية للمواضيع "العالية الفائدة".
- بعد ذلك، يرتّب المتصفّح المواضيع حسب عدد مرات ظهورها ضمن كل مجموعة.
- يتم اختيار أهم خمسة مواضيع من هذه القائمة المرتبة لتكون أهم مواضيع المستخدم في تلك الحقبة.
تعرض طريقة document.browsingTopics() بعد ذلك موضوعًا عشوائيًا من بين أهم خمسة مواضيع لكل حقبة، مع احتمال بنسبة% 5 أن يتم اختيار أي من هذه المواضيع بشكل عشوائي من التصنيف الكامل للمواضيع. في Chrome، يمكن للمستخدمين أيضًا إزالة مواضيع فردية أو محو سجلّ التصفّح لتقليل عدد المواضيع التي تعرضها واجهة برمجة التطبيقات. يمكن للمستخدمين أيضًا إيقاف واجهة برمجة التطبيقات.
يمكنك الاطّلاع على معلومات حول المواضيع التي تم رصدها خلال الفترة الحالية من صفحة chrome://topics-internals.
الخطوات التالية
الإعداد
تنفيذ المواضيع
انظر أيضًا
يمكنك الاطّلاع على مراجعنا لفهم Topics API على الويب بشكل أفضل.
- يمكنك الاطّلاع على عروض توضيحية وعروض تعاون وفيديوهات تفصيلية حول المواضيع.
- اطّلِع على قائمة خيارات Chrome المخصّصة للمطوّرين التي تتيح لهم تخصيص Topics API للاختبار.
- تعرَّف على كيفية تمكُّن المستخدمين والمطوّرين من التحكُّم في واجهة برمجة التطبيقات.
- اطّلِع على المراجع للحصول على خدمات تفسيرية فنية ودعم. طرح الأسئلة والتفاعل مع المستخدمين ومشاركة الملاحظات


